
In a subject standing in orthostatic position (upright) the apex of the lung shows higher V/Q ratio, while at the base of the lung the ratio is lower but nearer to the optimal value for reaching adequate blood oxygen concentrations. This has a major impact on the V/Q ratio: īecause the lung is centered vertically around the heart, part of the lung is superior to the heart, and part is inferior. If taken as a whole, the typical value is approximately 0.8. The actual values in the lung vary depending on the position within the lung. On the other side Ventilation-perfusion mismatch is the term used when the ventilation and the perfusion of a gas exchanging unit are not matched. This matching may be assessed in the lung as a whole, or in individual or in sub-groups of gas-exchanging units in the lung. If one were to consider humidified air (with less oxygen), then the ideal v/q ratio would be in the vicinity of 1.0, thus leading to concept of ventilation-perfusion equality or ventilation-perfusion matching.
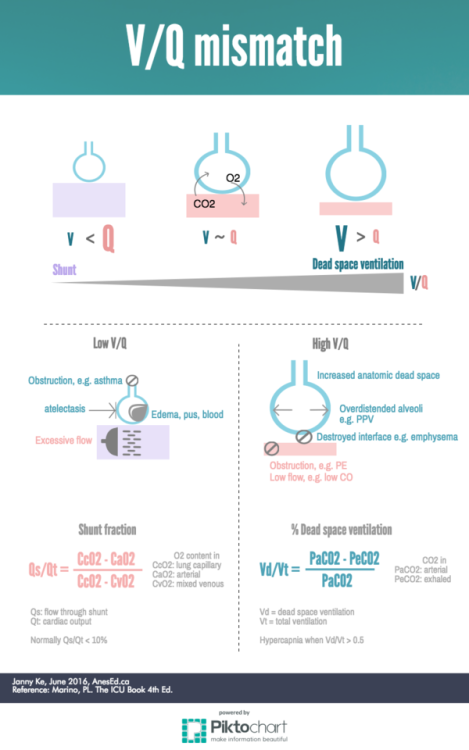
Therefore, under these conditions, the ideal ventilation perfusion ratio would be about 0.95. In the typical adult, 1 litre of blood can hold about 200 mL of oxygen 1 litre of dry air has about 210 mL of oxygen.
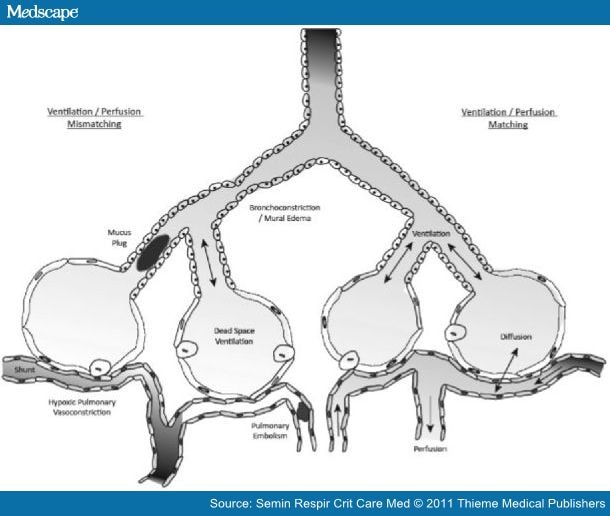
Ideally, the oxygen provided via ventilation would be just enough to saturate the blood fully. The V/Q ratio can be measured with a ventilation/perfusion scan.Ī V/Q mismatch can cause Type 1 respiratory failure. These two variables, V and Q, constitute the main determinants of the blood oxygen (O 2) and carbon dioxide (CO 2) concentration. The V/Q ratio can therefore be defined as the ratio of the amount of air reaching the alveoli per minute to the amount of blood reaching the alveoli per minute-a ratio of volumetric flow rates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
